作为一种最小和最轻的元素,氢可以可逆的进出VO2的间隙位置,并诱导其电子结构调制。长期以来人们主要关注低吸氢量的VO2,但对高储氢量的VO2 的性能并不清楚。近期韩国浦项科技大学Junwoo Son教授课题组研究了VO2中氢浓度对材料电学和光学性能的影响。相关成果发表于Nature materials期刊,题为“Reversible phase modulation and hydrogen storage in multivalent VO2 epitaxial thin films”(DOI: 10.1038/NMAT4692)。
通过脉冲激光沉积法在Al2O3或TiO2单晶基体上沉积一层30 nm厚的VO2薄膜,为了进一步提高吸氢量,再在VO2薄膜上沉积一层金属Pt。通过研究VO2的吸氢量与薄膜电阻之间的关系,发现在低温(< 80 oC)下VO2的薄膜电阻随吸氢量升高先降低再升高。转换机制为绝缘相的VO2®金属相的HxVO2®绝缘相的HVO2,且较VO2,HVO2透光率也提高。这种材料在基于质子的电子器件和高性能储氢体系有潜在的应用前景。
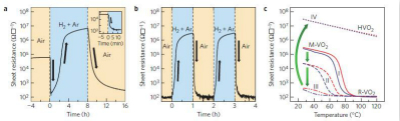
Fig.1 Dynamic resistivity modulation of HxVO2 by hydrogenation. a,b, In situ resistivity of (100)R-VO2 films on (0001) Al2O3 during hydrogenation and dehydrogenation as a function of time at 70 oC (a) and 120 oC (b). The inset in a represents the initial metallization by low hydrogen doping. Note the clear observation of pristine insulator–hydrogenated metal–hydrogenated insulator phase modulation during hydrogenation at 70 oC and reversible resistivity change of up to 105 during hydrogenation/dehydrogenation at 120 oC. c, Temperature-dependent sheet resistance in HxVO2 thin films from plot I to plot IV with increasing hydrogen content x.
|

